Have you ever stopped to think about the incredible power of the human brain? It’s a marvel of nature that has been studied for centuries, yet we still have so much to learn about its amazing capabilities. Despite all the technological advancements we’ve made, the human brain still outperforms even the most advanced supercomputers.
In this blog, we’re going to dive deep into the anatomy of the brain and explore how it functions. We’ll look at the different parts of the brain and what they’re responsible for, as well as the complex networks of neurons that allow us to think, feel, and experience the world around us.
Whether you’re a science enthusiast or simply curious about the inner workings of the human brain, you’ll find something to pique your interest in this blog. So, join us on this journey of discovery as we unravel the mysteries of the brain and gain a greater appreciation for the incredible organ that powers everything we do.
The Supercomputer
The human brain is often compared to a supercomputer, and for good reason. Both are capable of processing vast amounts of information, analyzing data, and making decisions based on that data. However, there are also some significant differences between the two.
For one, the human brain is much more adaptable than a supercomputer. While a computer is programmed to perform specific tasks, the brain can adapt and learn new things as needed. It is also capable of making intuitive leaps and creative connections that a computer simply cannot replicate.
Another difference is that the brain is able to process information in a way that is contextually relevant. This means that it is able to understand the meaning and significance of information in a way that a computer cannot. For example, if you see a stop sign, your brain instantly recognizes it as a signal to stop, whereas a computer would need to be specifically programmed to recognize the shape and color of a stop sign.
Despite the amazing capabilities of the human brain, there are still some things that computers are better at. For example, computers are much faster and more efficient at performing certain types of calculations and data processing tasks. However, even in these areas, the human brain is still able to outperform computers in certain situations.
Overall, it is the combination of the brain’s adaptability, intuition, and contextual understanding that makes it such a powerful and unique tool. While computers may be able to process information faster and more efficiently in some areas, they will never be able to replicate the amazing capabilities of the human brain.
Anatomy of the Brain
Alright, let’s dive into the fascinating world of the brain! In this section, we’ll explore the anatomy of the brain, starting with the most basic building block: the neuron.
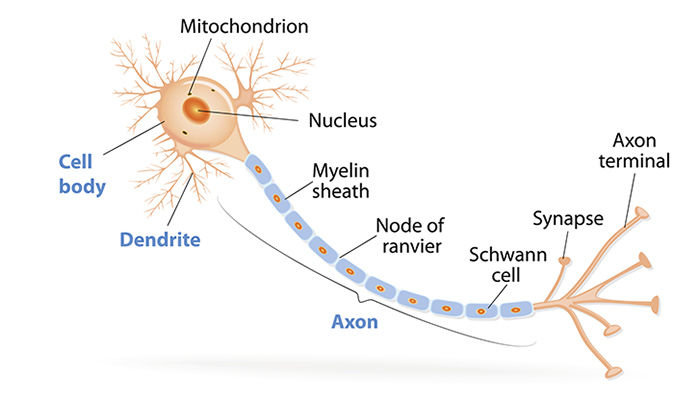
Did you know that the human brain is made up of approximately 100 billion neurons? These are specialized cells that are responsible for transmitting information throughout the brain and nervous system. Each neuron has three main parts: the soma, dendrites, and axon. The soma is the cell body, the dendrites receive signals from other neurons, and the axon sends signals to other neurons.
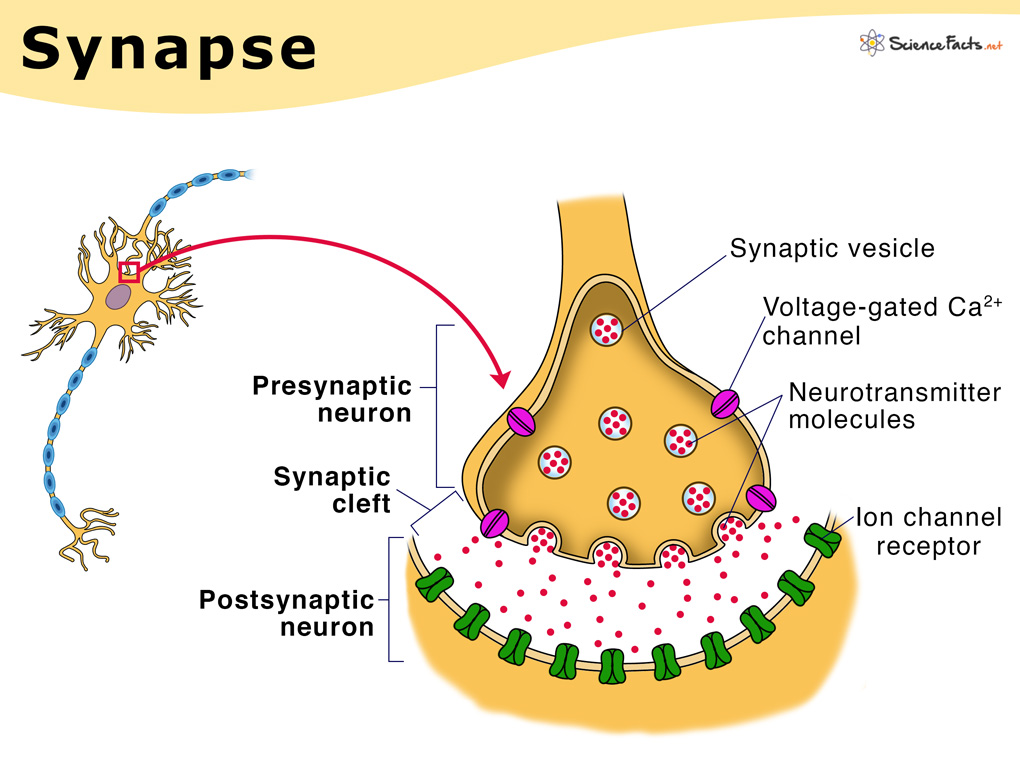
Neurons transmit information through electrochemical signals. When a neuron receives a signal from another neuron, it generates a tiny electrical impulse that travels down the axon. This impulse then triggers the release of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that carry the signal across the synapse (the gap between neurons).
The synapse is a crucial part of the brain’s processes, as it allows neurons to communicate with each other. When the neurotransmitter molecules cross the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the receiving neuron, it generates a new electrical impulse that travels down the receiving neuron’s axon. This process continues throughout the brain, forming complex neural networks that underlie our thoughts, behaviors, and experiences.
Understanding the anatomy of the brain and how neurons communicate with each other is essential in unlocking the mysteries of the mind. It’s amazing to think about how such complex processes can occur within our own heads!
How Signals are Transmitted
Have you ever wondered how your brain is able to send and receive signals at lightning-fast speeds? Well, in this section, we’ll explore just that.
The human brain is composed of approximately 100 billion neurons, which communicate with each other through electrochemical signals. When a neuron receives a signal, it processes the information and then decides whether or not to send its own signal to other neurons. This decision is determined by the neuron’s activation threshold.
The activation threshold is the minimum level of stimulation required for a neuron to fire and send a signal. If the stimulation level is below the threshold, the neuron remains inactive. However, if the stimulation level exceeds the threshold, the neuron will fire, sending a signal down its axon.
To ensure that signals travel quickly, neurons are wrapped in a fatty substance called the myelin sheath. This sheath acts as insulation, preventing signals from leaking out and slowing down. Signals are able to jump from one node of Ranvier to the next, bypassing areas where the myelin sheath is present.
Once a signal reaches the end of the axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters. These chemicals travel across the synaptic cleft, which is the small gap between the axon terminal and the receiving neuron’s dendrites. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the receiving neuron, causing it to become either more or less likely to fire its own signal.
Overall, the transmission of signals between neurons is a complex process that relies on the precise functioning of each individual neuron, as well as the connections between them.
Additional Points
The human brain is a complex and powerful organ that controls every aspect of our lives. While we’ve covered the basics of its anatomy and how it functions, there are a few additional points that are worth mentioning.
Firstly, it’s important to note that different regions of the brain are responsible for different functions. For example, the hippocampus is crucial for memory, the amygdala for emotion, and the cerebellum for movement. Understanding how these regions work together and independently can help us better understand the complex processes that occur in our brains.
Another fascinating aspect of the brain is its ability to create new neural connections and rewire itself. This process, known as neuroplasticity, allows the brain to adapt and change in response to new experiences and challenges. By engaging in new activities and learning new skills, we can strengthen our neural connections and improve our brain’s overall function.
We can also train and strengthen our brains through mental exercises such as meditation and cognitive training. These practices have been shown to improve memory, attention, and even the brain’s ability to regulate emotions.
Finally, it’s important to take care of our brains through healthy habits such as exercise, sleep, and proper nutrition. These habits not only promote overall physical health but also help support the brain’s function and protect against age-related decline.
The human brain is a marvel of nature with incredible abilities and potential. By learning more about how it functions and taking care of it through healthy habits, we can unlock its full potential and live our best lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the human brain is an incredibly complex and powerful organ that outperforms even the most advanced supercomputers. The 100 billion neurons in the brain work together to create electrochemical signals that allow us to think, feel, and move. The anatomy of the brain includes the soma, dendrites, and axon, which transmit these signals and form synapses. The synaptic cleft plays an important role in the brain’s processes by allowing neurotransmitters to pass signals from one neuron to another.
The brain’s ability to send electrical signals through the brain, with the help of the myelin sheath, and to utilize neurotransmitters, allow it to understand things that computers cannot. The brain is capable of creativity, emotions, and complex decision-making, which are not currently replicable by computers.
As we continue to learn more about the brain, we can gain a better understanding of how it works and how we can optimize its capabilities. Learning new things, practicing mindfulness, and staying physically active are just a few ways we can improve the health and function of our brains.
In conclusion, take the time to learn more about the incredible capabilities of your brain. You may be surprised at what you can achieve with such an amazing organ at your disposal.